Evolution of Block Chain Technology and its Implication to the IT industry
mentorblendofficials@gmail.com
December 22, 2024
To date, the advancement of blockchain technology has matured significantly. Originally linked with digital currency, including Bitcoin, Block chain has become a revolutionary in many sectors especially IT. In this blog post, the reader will learn more about the origins, evolution, and significance of blockchain in the world of IT. Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the recorded transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This ensures transparency, security, and immutability in data management. Blockchain technology powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum and has expanded to various other applications across industries.
The History of Blockchain Technology
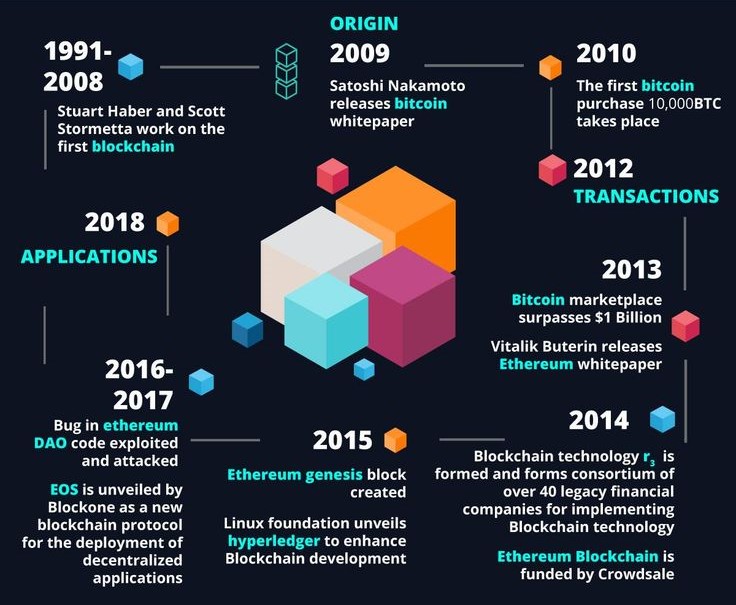
The blockchain is the biggest innovation in computer science—the most important innovation—since the invention of the Internet.
Don Tapscott – Co-Author of Blockchain Revolution
Key features of early blockchain technology includes
Blockchain on its part was first considered in 2008 by an entity identified only as Satoshi Nakamoto to act as the technical foundation for Bitcoin. Therefore, the main new idea was to develop the distributed and unchangeable register system that is free from middlemen.
Key features of block chain includes:
- Decentralization: Information also established in a network of digital nodes.
- Immutability: Note that, once data has been captured somewhere, amending it is out of the question.
- Transparency: Such transactions that are known to all the people that take part in the network.
How blockchain is evolving beyond the idea of cryptocurrencies?
Over several years, people realized that there were many more applications of the distributed ledger technology known as the blockchain. Major milestones include:
- Smart Contracts: Ethereum used programmable contracts that work on their own once the program set conditions are achieved; used for decentralized applications (dApps).
- Permissioned Blockchains: Specifically tailored for the enterprise, such blockchains open only limited access but do not lose the essential properties of the blockchain.
- Interoperability: Ultimately, new innovative blockchains or solutions such as Polkadot and Cosmos appeared to link multiple blockchains to initiate data and value sharing.
- Scalability Solutions: Advanced layers come in the form of Lightning Network and sharding to tackle scalability as a problem, bringing out the practicality of blockchain network in application across vast industries.
Impact on the IT Industry
Blockchain has impacted several areas of IT, providing solutions where none was seen before. Here’s how:
1. Enhanced Security
It is impossible to hack Blockchain because it uses algorithms to store and encase the data. Applications include:
- Secure Identity Management: Using a decentralized identity to protect personal information.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining the entity and integrity of the data in specially business & finance, health care & medicine or any other field.
2. Decentralized Infrastructure
Information technology systems have in the past adopt solutions that are based on central data hosts –often implying on single points of failure. Blockchain introduces:
- Decentralized Storage: Some examples of cryptographic systems include Internet Protocol File System and Filecoin that provide secure distributed file system.
- Resilient Networks: Thus, peer-to–peer communication scheduling is critical in maintaining uninterrupted services.
3. Smart Contracts for Automation
In theory, smart contracts make life easier by coming in with fewer go-betweens and cutting down on expenses and time. Examples include:
- Supply Chain Management: The automated system of inventory tracking and payments.
- Legal Agreements: It refers to enforcing terms without the into of a human the power of attorney allows the agent to make an enforce the terms automatically.
4. New Business Models
Blockchain has enabled innovative IT solutions:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Provision of financial service without the aid of any formal bank.
- Tokenization: Building digital tokens for actual objects ranging from art to properties.
- Web3: A vision where the user owns everything that is being created and shared within the internet.
How Block Chain Works?
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure, transparent, and immutable manner. It operates by grouping data into blocks, which are linked together in a chronological sequence to form a chain. Each block contains a set of transactions, a unique cryptographic hash of its data, and the hash of the previous block, creating a secure connection between blocks. When a user initiates a transaction, it is broadcast to a network of nodes (computers), which validate it using consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), or others. Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block, which is then linked to the existing blockchain. This decentralized structure ensures that no single entity controls the data, while its cryptographic nature makes it resistant to tampering or unauthorized modifications. Every participant in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, enhancing transparency and trust. Blockchain’s robust design has revolutionized industries by enabling applications like cryptocurrencies, supply chain tracking, secure voting systems, and smart contracts, making it a cornerstone of the modern digital economy.
Areas of Concern and Intersection
While blockchain has immense potential, it faces challenges:
- Scalability: Many of the current systems bear the immense pressures of high transaction volumes.
- Energy Consumption: Both mining and consensus techniques such as Proof of work is notorious for power consumption.
- Regulation: Of major challenge is the irregularity of the laws in different states.
Future developments directions include:
- Switch to participation in eco-friendly consensus mechanism such as the Proof of Stake.
- Novelties in the field of post-quantum cryptography.
- Growing popularity within applications from new domains such as IoT and AI.
Blockchain technology has come as a revolution in the current Information Technology landscape promising unparalleled opportunities for innovation, security and efficiency. Over the time, the technology is likely to advance to achieve further probable results putting IT at the direction of decentralization and transparency. It has therefore become incumbent to enter the world of blockchain for both IT professionals and businesses merely for the purpose of competitiveness in the increasingly digital age.
nice blog